Zero trust is a cybersecurity framework for protecting modern IT infrastructure and data. It demands strict identity verifications for every individual and device trying to access the IT network. It implies both internal & external devices be authenticated, authorized, and continuously validated before granting access to the organization's IT network.
Additionally, security configurations and posture validation are ensured regardless of whether the user is within or outside the IT network. Zero trust is both a vision and security principle for organizations.
The term zero trust is now predominant in security vendor marketing and in security guidance from governments. According to Gartner, 60% of organizations will embrace Zero Trust as a starting point for security by 2025.
Why Zero-Trust model?
With many high-level data breaches, zero trust interest and adoption have increased drastically in recent years. Additionally, the need for better cybersecurity practices and the global pandemic spurred an unprecedented demand for secured remote access technologies.
In the past, large enterprises relied on firewalls to build fences around their IT network. With this model, the off-site user accesses their IT resources remotely through a VPN to create a secure tunnel into the network. Here the major challenge is when the wrong hands misuse VPN login credentials, as happened in one of the largest American pipeline data breaches. Thus, the Zero Trust model is necessary for modern computing networks. It is a holistic cybersecurity approach that comprises several principles and technologies. Primarily, it denies access to an enterprise's digital resources by default and grants only authenticated users and devices to the IT network.
Modern Approach to Zero-Trust Security
The zero-trust framework has gained traction in the data center industry due to the “work from anywhere” norms driven by the pandemic. Adopting advanced cyber security solutions such as zero trust and extended detection and response (XDR) can boost security resilience to businesses.
According to Gartner Study, Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is the fastest-growing segment in network security and is forecast to grow 31% in 2023. It is also the security framework of the future and will replace virtual private networks by 2025.
Zero-Trust for the cloud:
The digital transformation journey depends on the strength of the hybrid cloud environment. Organizations should deploy security consistently across all cloud environments. It brings resilience and confidence to business operations.
A zero-trust approach helps enterprises modernize business operations. It enables businesses to adapt to datasets, users, and workloads irrespective of where they are positioned. In other words, hybrid cloud protection with zero trust security results in centralized visibility and helps business organizations to innovate and enforce security policies without any delays.
How Is Zero-Trust Security Implemented?
Organizations should design a robust Zero Trust architecture to mitigate risks across all computing environments by establishing identity verification, validating device compliance before granting access, and ensuring the least privileged access to only authorized resources.
The implemented Zero Trust security should help:
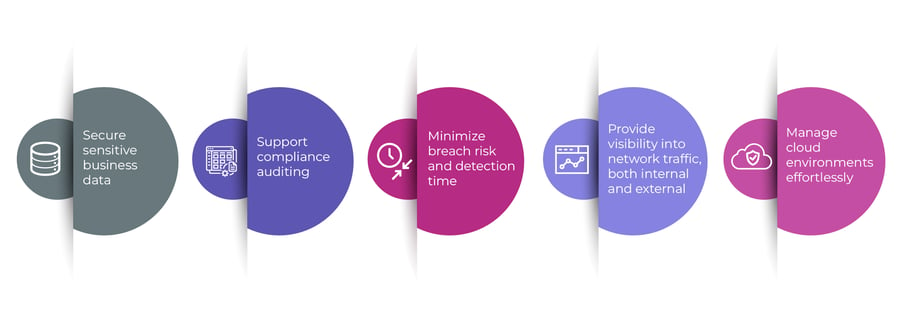
Zero-trust ensures transactions between devices, users, IT networks, and software applications are trustworthy before it occurs. The ideal zero-trust environment essentials are:
Multi-factor authentication:
All identities are validated and secured with multi-factor authentication. It eliminates password expiration. In addition, the use of biometrics ensures strong authentication for user-backed identities.
IT Assets Validation:
All hardware and software assets are managed and validated as healthy. To access organizational resources, all device types and operating systems should meet the minimum health state.
Telemetry and pervasive data:
The automatic measurement and remote data transmission help to understand the existing security state and gaps. You can also validate the impact of new controls and compare data across all software applications in the computing environment. In Zero Trust security, robust & standardized auditing, telemetry, and monitoring capabilities are major requirements across IT assets in an IT network.
Least privilege access:
The need to enforce least privilege access for a few applications, services, and infrastructure is high to perform some security operations. Any identity and access management solutions that offer broad access to any organization's critical IT infrastructure without any segmentation must be avoided.
How Aujas Does Zero Trust Security?
Aujas is ready to implement Zero Trust across your IT infrastructure for all types of users, employees, external devices, partners, and customers.
Organizations can monitor network traffic, respond to activity, and examine the risks users or applications may pose to your network. In addition, it helps your in-house IT security team to guard all the assets and secure the IT network.
To know more about Zero Trust security services, talk to our security experts at contact@aujas.com.