Why Blockchain?
With majority of companies being stuck in the exploration phase, Blockchain has a big potential of transforming operation models of multiple industries. Blockchain technology is rapidly booming in Financial Services sector and IDC predicts that at least 25% of the global banks will incorporate Blockchain in their operations by 2019. However, it is not only the financial sector that Blockchain is set to disrupt; manufacturing, healthcare, retail, telecom, government, and education will also see rapid evolution and acceptance of this technology.
According to the World Economic Forum, investing on Blockchain startups is estimated at US$1.4B in the past 3 years. The emergence of multiple Blockchain platforms through companies and start-ups such as Private (e.g. Multichain) or Consortium (e.g. HyperLedger) or Public (e.g. Ethereum) is providing organizations at different avenues to meet their requirements.
Financial companies are taking different approaches to adopt Blockchain by establishing Blockchain labs and developing in-house projects (e.g. Citibank developed Citicoin, BNY Mellon is backing up bank transactions with Blockchain).
Adoption of Blockchain has few challenges, which includes understanding and implementation of the technology, lack of standards and robust platforms. The applications to run on Blockchain is a future important aspect of Blockchain technology.
Blockchain Adoption by Different Industry Sectors
The potential of Blockchain technologies to grow across various domains can be illustrated with a few possible use cases as shown below:
- Financial Services – Features such as smart contracts, real-time transactions, digital currencies can impact on global remittance, fraud detection, banking experience etc.
- Manufacturing, Supply Chain – Goods inventory and product origin tracking, inventory, multi-party agreements could be implemented using smart contracts.
- Healthcare – Smart contracts can implement automated claim processing. Digital identification can enhance patient records privacy. Medicinal inventory trafficking could be trusted to eliminate fraud.
- Telecom and Communication- Distributed cloud storage, billing systems automation and call detail record verification are different functionalities that can be implemented.
- Internet of Things – Blockchain technology would enable automation, decentralization and secure transactions between IoT devices.

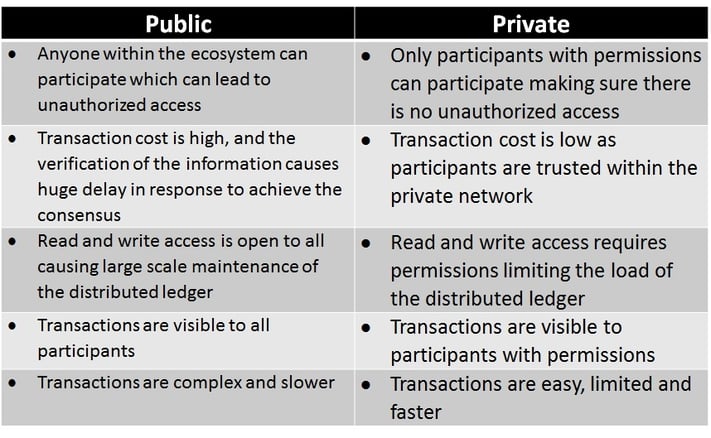
Advantage of Private Blockchain over Public blockchain
Notable Hacks in Public Blockchain
- Nicehash hack, Dec 2017 - Cryptocurrency amounting to $64 million Bitcoin is said to be stolen from cryptocurrency mining marketplace NiceHash, emptying its entire bitcoin wallet.
- CoinDash ICO hack, July 2017 - CoinDash website was compromised merely 3 minutes after the sale started. The address for sending investments was changed to a fake address and investments were routed to the attacker's account. Around $7.4 million Ethereum was stolen during this hack.
- Krypton (KR) & Shift (SHF), Aug 2016 - Attackers targeted Ethereum-based Blockchains likes the cryptocurrencies, Krypton (KR) and Shift. The attackers were able to exploit the Blockchain with a two-step attack: overpowering the network with a 51% attack to ensure rollback on transactions and spending the coins twice; and employing DDoS nodes to enhance network power. The attack led to the loss of 21,465 KR, $3000 at the time.
- Steemit, July 2016 - The Blockchain-based blogging platform, was hacked. Vulnerability on the Web browser front end and not on the cryptocurrency itself led to this attack. Around 250 user accounts were compromised, resulting in the loss $85,000 worth of Steem Dollars and cryptocurrency Steem.
- The DAO, May 2016 - Blockchain based venture capital, The DAO – an Ethereum Project, was hacked for $60 million.
Top 6 Security issues in private blockchain ecosystem:
With the rapid growth of technology, there are many loopholes that are being discovered on the go. Organizations implementing such solutions could have infrastructure issues with an insecure Blockchain technology.
Highlighted below are some of the security issues during Blockchain implementation:
- Orphan Consensus forks in Blockchain - Private Chain ledger network may get split and replicated into parallel fork chains creating ambiguity among child blocks for parallel parent fork chains. This replication is susceptible to double spending/replay attacks in parallel fork chains.
- Weak Permissioned network - Ledgers could be susceptible to DoS, transaction spamming attacks or control over blocks for creation if proper MSPare not set for the private/permissioned Blockchain network.
- Weak implementation of PKI based cryptography and Hashing - Key distribution must have done securely for generating and distributing keys amongst different entities that are within the network. If cryptographic keys are not stored or maintained properly, it could cause compromise and disclosure of private keys leading to fraudulent transactions or loss of assets/values. This will lead to compromising the integrity and privacy of the operations.
- Undefined Smart contracts - Code Vulnerabilities like call stack, stack size limit, reentrancy, malicious libraries, type casts, open sensitive information might deviate smart contracts’ intended behavior to malicious transactions or even unintended take over for further compromise.
- Transaction Tampering - If transaction and block policies are mutable and not tamperproof it may allow alteration of data for blocks without the approval of other nodes in the chain.
- Security Governance - Private Blockchain with permissions and having a closed environment fails to follow organizational decision-making process and protocols of how the ecosystem is to be created, developed or changed.
Mitigation Strategy to secure private Blockchain
- Developing Strategic Blockchain design - Exploring the feasibility and developing distributed hyper-ledger technology would help to develop a design customized to each domain and firm. Identifying the factors helps in development with the constraints required on scalability, required alterations accounting the transparency.
- Endorsing policies- In Private Blockchain Network, the number of confirmation requirements for validating transaction can be increased and it must be validated from trusted and authenticated business participant entities only. Also need to focus on strengthening techniques such as profiling, monitoring and detecting regular behavioral patterns based on transaction history.
- Cryptography management - A detailed process on cryptography to be developed and aligned, based on the customization required for implementing Blockchain and integrating it with the concerned domain. The Standard procedure to comprise of steps for securely generating and distributing keys amongst different entities which may be within or outside, encryption and decryption methodology, digital signature creation, verification, message authentication etc.
- Limiting Access Rights - It is advisable to identify and gauge all blocks or transactions in private Blockchain that need to be restricted to business participants based on their access rights. Only required concerned parties should be responsible to preserve privacy and confidentiality.